- Description
- Key Ingredients & Benefits
- Usage & Directions
- Quality Standards
- Warnings
- Sources
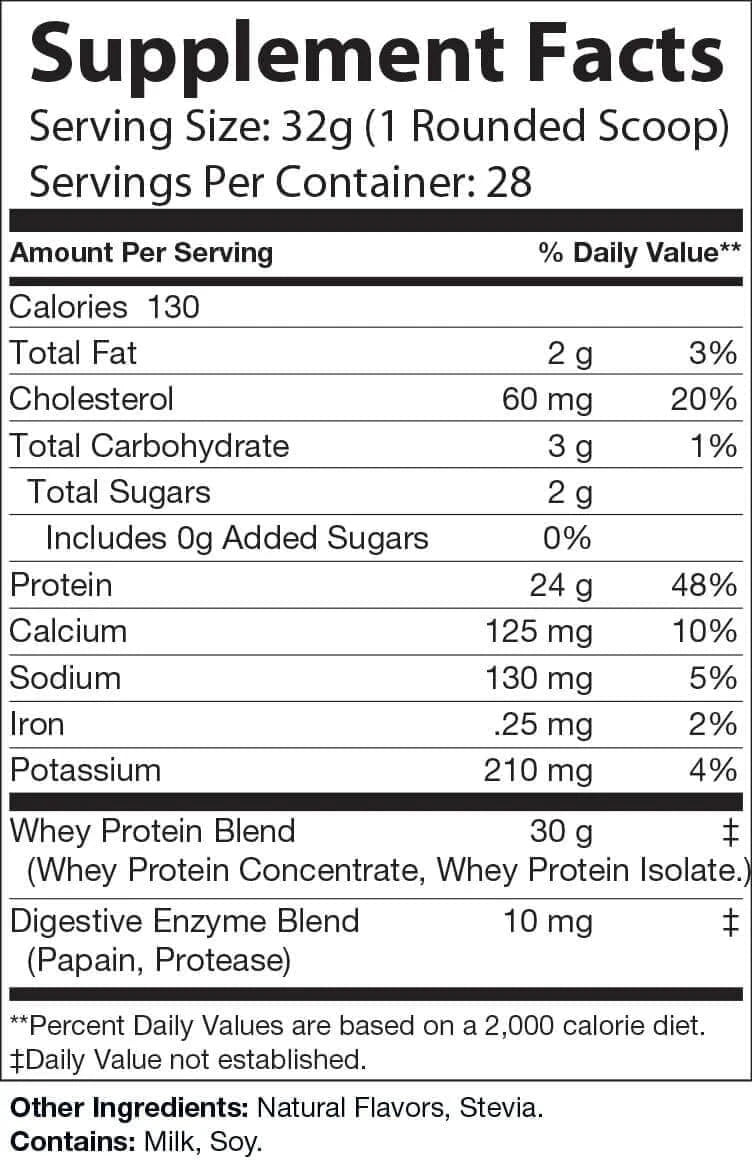
NC-FORCE Natural Whey offers a high-quality protein solution with 75% protein per scoop — powered by a blend of whey isolate, BCAAs, and digestive enzymes including papain and protease. Ideal for post-workout recovery, it supports muscle maintenance, nutrient uptake, and daily wellness without unnecessary fillers.
-Muscle Support: Provides complete protein and amino acids to help maintain lean muscle after workouts.
-Digestive-Friendly Formula: Includes enzymes to support protein breakdown and nutrient absorption.
-Clean Fuel: Naturally low in fat and sugar, perfect for your fitness and nutrition goals.
-Everyday Wellness: Helps meet your daily protein needs to support an active lifestyle.
- Whey Protein Concentrate: High-quality, bioavailable protein that supports muscle growth, immunity, and digestion. Rich in glutathione for antioxidant benefits.
- Whey Protein Isolate: Faster absorption, fewer fats and sugars, ideal for quick protein synthesis and recovery post-workout.
- BCAAs (Leucine, Isoleucine, Valine): Essential for muscle protein synthesis and preventing muscle breakdown.
Mix one rounded scoop with 4-6 oz of water, milk, or your favorite beverage. Adjust liquid amount to taste preference. Best taken immediately after a workout for optimal muscle recovery.
- Our Formula: High-quality, bioavailable whey protein concentrate and isolate, tested for purity.
-*These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. -Tamper Seal: Use only if the seal is intact. Consult your health care practitioner if you are pregnant or nursing, taking medications, or have a medical condition, before taking this or any other product. -Store in a cool, dry place. Keep out of reach of children.
43. Teixeira, F. J., Santos, H. O., Howell, S. L., & Pimentel, G. D. (2019). Whey protein in cancer therapy: A narrative review. Pharmacological research , 144 , 245–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2019.04.019
44. Colonetti, T., Grande, A. J., Milton, K., Foster, C., Alexandre, M. C., Uggioni, M. L., & Rosa, M. I. (2017). Effects of whey protein supplement in the elderly submitted to resistance training: systematic review and meta-analysis. International journal of food sciences and nutrition , 68 (3), 257–264. https://doi.org/10.1080/09637486.2016.1232702
45. Marshall K. (2004). Therapeutic applications of whey protein. Alternative medicine review : a journal of clinical therapeutic , 9 (2), 136–156.
46. A Castro, L. H., S de Araújo, F. H., M Olimpio, M. Y., B de B Primo, R., T Pereira, T., F Lopes, L. A., B S de M Trindade, E., Fernandes, R., & A Oesterreich, S. (2019). Comparative Meta-Analysis of the Effect of Concentrated, Hydrolyzed, and Isolated Whey Protein Supplementation on Body Composition of Physical Activity Practitioners. Nutrients , 11 (9), 2047. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11092047