- Description
- Key Ingredients & Benefits
- Usage & Directions
- Quality Standards
- Warnings
- Sources
Adaptogen+ is a premium herbal blend featuring well-known adaptogens like Rhodiola, Eleuthero, and Maca — formulated to support a balanced lifestyle and daily performance. Ideal for professionals and high-output individuals, this formula is crafted for those seeking calm focus and day-to-day resilience.
-Mind-Body Balance: Adaptogens traditionally used to help the body adapt to occasional physical and mental stressors.
-Daily Focus & Energy Support: Designed to complement busy routines with gentle, plant-based vitality.
-Rooted in Tradition: Features globally recognized herbs known for their use in holistic wellness practices.
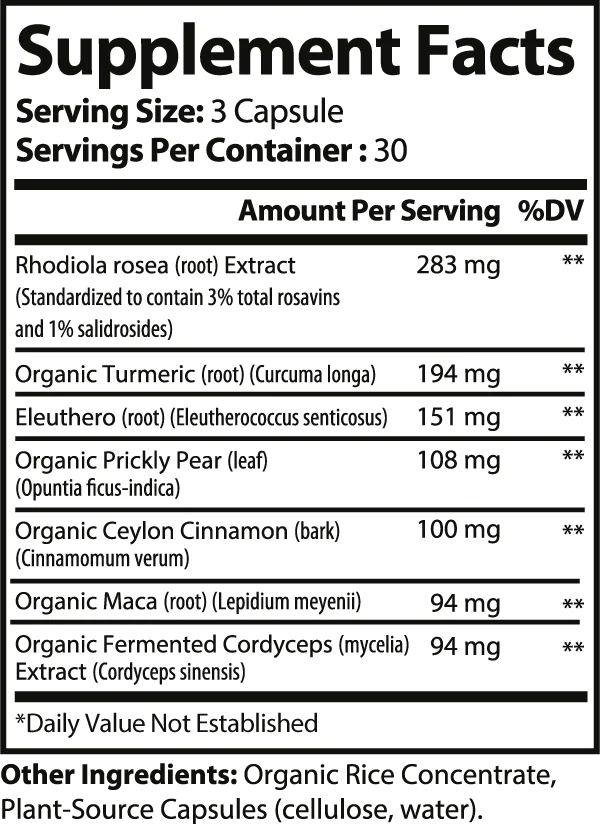
Rhodiola Rosea Extract: Enhances cognitive function, supports immune health, reduces inflammation, and promotes cardiovascular wellness.
Organic Turmeric: Known for its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and cardio-protective effects, Turmeric also supports blood sugar regulation, liver health, and joint function.
Eleuthero Root: Balances stress hormones and support healthy cortisol, testosterone, and estrogen levels.
Organic Prickly Pear Leaf: Reduces oxidative damage and boosts antioxidant levels, supporting immune health.
Organic Ceylon Cinnamon: Regulates blood sugar, improves insulin sensitivity, and promotes cardiovascular health.
Maca Root: Supports hormonal health, enhancing libido, alleviating menopausal symptoms in women, and boosting sperm count in men.
Fermented Cordyceps: Enhances stamina, immune response, and antioxidant support and may reduce chronic fatigue and inflammation
Take 3 capsules at breakfast or before 2 P.M., or as directed by a health professional.
Manufactured in the USA in a GMP-certified, FDA-registered facility, Adaptogen+ meets world-class standards for purity and effectiveness, outperforming many formulas that rely on low-cost, less pure ingredients.
-*These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. -Tamper Seal: Use only if the seal is intact. Consult your health care practitioner if you are pregnant or nursing, taking medications, or have a medical condition, before taking this or any other product. -Store in a cool, dry place. Keep out of reach of children.
12. Dording, C. M., Schettler, P. J., Dalton, E. D., Parkin, S. R., Walker, R. S., Fehling, K. B., Fava, M., & Mischoulon, D. (2015). A double-blind placebo-controlled trial of maca root as treatment for antidepressant-induced sexual dysfunction in women. Evidence-based complementary and alternative medicine: eCAM , 2015 , 949036. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/949036
13.Pu, W. L., Zhang, M. Y., Bai, R. Y., Sun, L. K., Li, W. H., Yu, Y. L., Zhang, Y., Song, L., Wang, Z. X., Peng, Y. F., Shi, H., Zhou, K., & Li, T. X. (2020). Anti-inflammatory effects of Rhodiola rosea L.: A review. Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine & pharmacotherapie , 121 , 109552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109552
117. Chilelli, N. C., Ragazzi, E., Valentini, R., Cosma, C., Ferraresso, S., Lapolla, A., & Sartore, G. (2016). Curcumin and Boswellia serrata Modulate the Glyco-Oxidative Status and Lipo-Oxidation in Master Athletes. Nutrients , 8 (11), 745. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8110745
118. Barzegar, A., & Moosavi-Movahedi, A. A. (2011). Intracellular ROS protection efficiency and free radical-scavenging activity of curcumin. PloS one , 6 (10), e26012. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0026012
119. Banik, U., Parasuraman, S., Adhikary, A. K., & Othman, N. H. (2017). Curcumin: the spicy modulator of breast carcinogenesis. Journal of experimental & clinical cancer research : CR , 36 (1), 98. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-017-0566-5
120. Suhett, L. G., de Miranda Monteiro Santos, R., Silveira, B., Leal, A., de Brito, A., de Novaes, J. F., & Lucia, C. (2021). Effects of curcumin supplementation on sport and physical exercise: a systematic review. Critical reviews in food science and nutrition , 61 (6), 946–958. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2020.1749025
121. Pivari, F., Mingione, A., Brasacchio, C., & Soldati, L. (2019). Curcumin and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Prevention and Treatment. Nutrients , 11 (8), 1837. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081837
122. Ashtary-Larky, D., Rezaei Kelishadi, M., Bagheri, R., Moosavian, S. P., Wong, A., Davoodi, S. H., Khalili, P., Dutheil, F., Suzuki, K., & Asbaghi, O. (2021). The Effects of Nano-Curcumin Supplementation on Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Disease: A GRADE-Assessed Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Clinical Trials. Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland) , 10 (7), 1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10071015
123. Mata, I., Mata, S., Menezes, R., Faccioli, L. S., Bandeira, K. K., & Bosco, S. (2020). Benefits of turmeric supplementation for skin health in chronic diseases: a systematic review. Critical reviews in food science and nutrition , 1–15. Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2020.1798353
166. Hariri, M., & Ghiasvand, R. (2016). Cinnamon and Chronic Diseases. Advances in experimental medicine and biology , 929 , 1–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-41342-6_1
368. Tesoriere, L., Butera, D., Pintaudi, A. M., Allegra, M., & Livrea, M. A. (2004). Supplementation with cactus pear (Opuntia ficus-Indica) fruit decreases oxidative stress in healthy humans: a comparative study with vitamin C. The American journal of clinical nutrition , 80 (2), 391–395. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/80.2.391