- Description
- Key Ingredients & Benefits
- Usage & Directions
- Quality Standards
- Warnings
- Sources
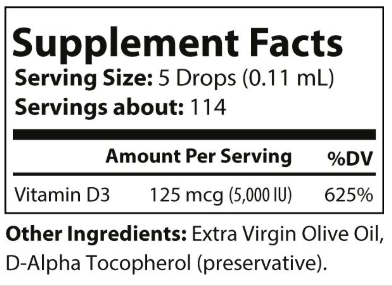
Vita D3 Ultra is a premium vitamin D3 supplement expertly formulated to support bone health, immune function, cardiovascular health, blood sugar regulation, hormonal balance, cognitive health, and more. With 5,000 IU per serving of natural-source vitamin D3 in a base of extra virgin olive oil, Vita D3 Ultra offers optimal bioavailability. This pure, high-potency formula is free from artificial additives and crafted to meet the highest standards, making it a trusted choice for healthcare professionals.
Vitamin D3: Supports bone health, immune function, cardiovascular health, hormonal regulation, exercise performance, and cognitive health. Vitamin D3 also helps enhance mood, promote muscle growth, and reduce inflammation.
Take 5 drops daily or as directed by a healthcare professional.
Quality Assurance: Made in the USA in an FDA-registered facility, GMP certified, and third-party tested for purity.
Purity and Efficacy: Blended with extra virgin olive oil, free from artificial additives, ensuring the most bioavailable and effective vitamin D3.
Premium Quality: Vita D3 Ultra is manufactured to GMP standards, using high-quality, tested ingredients, whereas cheaper alternatives may contain fillers and heavy metals.
-*These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. -Tamper Seal: Use only if the seal is intact. Consult your health care practitioner if you are pregnant or nursing, taking medications, or have a medical condition, before taking this or any other product. -Store in a cool, dry place. Keep out of reach of children.
77. Chang, S. W., & Lee, H. C. (2019). Vitamin D and health - The missing vitamin in humans. Pediatrics and neonatology , 60 (3), 237–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pedneo.2019.04.007
78. Zhang, Y., Fang, F., Tang, J., Jia, L., Feng, Y., Xu, P., & Faramand, A. (2019). Association between vitamin D supplementation and mortality: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ (Clinical research ed.) , 366 , l4673. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.l4673
79. Pilz, S., Frisch, S., Koertke, H., Kuhn, J., Dreier, J., Obermayer-Pietsch, B., Wehr, E., & Zittermann, A. (2011). Effect of vitamin D supplementation on testosterone levels in men. Hormone and metabolic research = Hormon- und Stoffwechselforschung = Hormones et metabolisme , 43 (3), 223–225. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0030-1269854
367. Sugden, J. A., Davies, J. I., Witham, M. D., Morris, A. D., & Struthers, A. D. (2008). Vitamin D improves endothelial function in patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus and low vitamin D levels. Diabetic medicine : a journal of the British Diabetic Association , 25 (3), 320–325. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-5491.2007.02360.x
368. Oudshoorn, C., Mattace-Raso, F. U., van der Velde, N., Colin, E. M., & van der Cammen, T. J. (2008). Higher serum vitamin D3 levels are associated with better cognitive test performance in patients with Alzheimer's disease. Dementia and geriatric cognitive disorders , 25 (6), 539–543. https://doi.org/10.1159/000134382
369. Terock, J., Hannemann, A., Van der Auwera, S., Janowitz, D., Spitzer, C., Bonk, S., Völzke, H., & Grabe, H. J. (2020). Posttraumatic stress disorder is associated with reduced vitamin D levels and functional polymorphisms of the vitamin D binding-protein in a population-based sample. Progress in neuro-psychopharmacology & biological psychiatry , 96 , 109760. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2019.109760