- Description
- Key Ingredients & Benefits
- Usage & Directions
- Quality Standards
- Warnings
- Sources
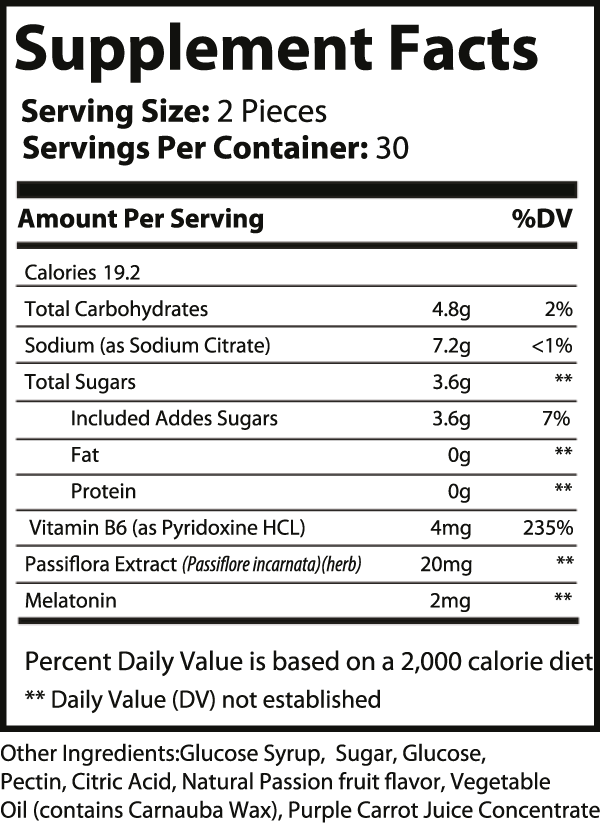
SleepZen Gummies are a soothing nighttime formula made with melatonin, passionflower extract, and vitamin B6 — a gentle, non-habit-forming addition to your evening routine. These gummies are designed to help you unwind and ease into rest with calm support.
-Evening Wind-Down Formula: Crafted to support natural relaxation and help you transition from busy days to peaceful nights.
-Botanical Blend: Features calming plant-based ingredients traditionally used for nighttime balance.
-Tasty & Easy to Take: Great-tasting gummies that fit right into your self-care routine — no capsules needed.
Vitamin B6:
- Supports blood sugar regulation, cardiovascular health, and immune function.
- Acts as an antioxidant, reducing inflammation and oxidative stress.
Passionflower Extract:
- Reduces stress and anxiety while promoting a positive mood and better sleep by regulating GABAA receptors, which control sleep patterns.
Melatonin:
- Helps regulate healthy sleep cycles, supports immune function, and acts as a powerful antioxidant.
Take two (2) gummies before bedtime or as directed by a healthcare provider. Do not exceed the recommended dose
- High-Quality Ingredients: Our formula is third-party tested for heavy metals and impurities, ensuring safety and purity. Produced in the USA in a GMP-certified, FDA-registered facility, SleepZen Gummies meet world-class standards – a level achieved by only 1% of supplements on the market.
-*These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. -Tamper Seal: Use only if the seal is intact. Consult your health care practitioner if you are pregnant or nursing, taking medications, or have a medical condition, before taking this or any other product. -Store in a cool, dry place. Keep out of reach of children.
38. Ueland, P. M., McCann, A., Midttun, Ø., & Ulvik, A. (2017). Inflammation, vitamin B6, and related pathways. Molecular aspects of medicine , 53 , 10–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mam.2016.08.001
39. Bird R. P. (2018). The Emerging Role of Vitamin B6 in Inflammation and Carcinogenesis. Advances in food and nutrition research , 83 , 151–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.afnr.2017.11.004
40. Mascolo, E., & Vernì, F. (2020). Vitamin B6 and Diabetes: Relationship and Molecular Mechanisms. International journal of molecular sciences , 21 (10), 3669. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21103669
248. Janda K, Wojtkowska K, Jakubczyk K, Antoniewicz J, Skonieczna-Żydecka K. Passiflora incarnata in Neuropsychiatric Disorders-A Systematic Review. Nutrients. 2020 Dec 19;12(12):3894. doi: 10.3390/nu12123894. PMID: 33352740; PMCID: PMC7766837.
256. Xie, Z., Chen, F., Li, W. A., Geng, X., Li, C., Meng, X., Feng, Y., Liu, W., & Yu, F. (2017). A review of sleep disorders and melatonin. Neurological research , 39 (6), 559–565. https://doi.org/10.1080/01616412.2017.1315864
257. Vural, E. M., van Munster, B. C., & de Rooij, S. E. (2014). Optimal dosages for melatonin supplementation therapy in older adults: a systematic review of current literature. Drugs & aging , 31 (6), 441–451. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40266-014-0178-0
258. Zarezadeh, M., Khorshidi, M., Emami, M., Janmohammadi, P., Kord-Varkaneh, H., Mousavi, S. M., Mohammed, S. H., Saedisomeolia, A., & Alizadeh, S. (2020). Melatonin supplementation and pro-inflammatory mediators: a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. European journal of nutrition , 59 (5), 1803–1813. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-019-02123-0