- Description
- Key Ingredients & Benefits
- Usage & Directions
- Quality Standards
- Warnings
- Sources
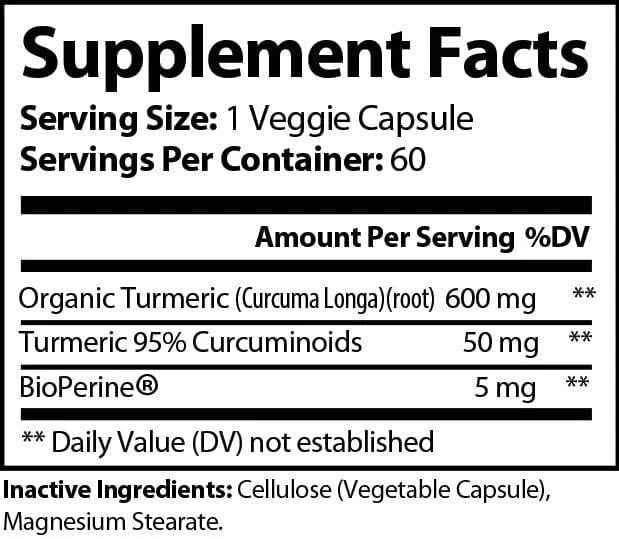
Turmeric+ BioPerine is a premium supplement designed to promote joint health, reduce inflammation, enhance flexibility, and support cardiovascular, immune, and cognitive health. With organic turmeric and ginger combined with the absorption-enhancing BioPerine®, this formula maximizes effectiveness for optimal wellness.
Organic Turmeric:
-Reduces inflammation and joint pain while improving flexibility.
-Acts as a powerful antioxidant and supports cardiovascular, immune, and blood sugar health.
BioPerine® (Black Pepper): Enhances the absorption and bioavailability of turmeric and curcumin.
Calcium: Supports bone health, muscle function, and cardiovascular health.
Take one veggie capsule twice daily, preferably 20–30 minutes before meals, or as directed by your healthcare professional.
-Science-Backed Formula: Combines organic turmeric, curcumin, and BioPerine® for superior absorption and efficacy.
-Purity Assured: Made in the USA in an FDA-registered, GMP-certified facility and third-party tested for impurities.
-Unmatched Quality: Only 1% of supplements meet the rigorous standards achieved by Turmeric+ BioPerine.
-*These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. -Tamper Seal: Use only if the seal is intact. Consult your health care practitioner if you are pregnant or nursing, taking medications, or have a medical condition, before taking this or any other product. -Store in a cool, dry place. Keep out of reach of children.
118. Barzegar, A., & Moosavi-Movahedi, A. A. (2011). Intracellular ROS protection efficiency and free radical-scavenging activity of curcumin. PloS one , 6 (10), e26012. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0026012
119. Banik, U., Parasuraman, S., Adhikary, A. K., & Othman, N. H. (2017). Curcumin: the spicy modulator of breast carcinogenesis. Journal of experimental & clinical cancer research : CR , 36 (1), 98. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-017-0566-5
120. Suhett, L. G., de Miranda Monteiro Santos, R., Silveira, B., Leal, A., de Brito, A., de Novaes, J. F., & Lucia, C. (2021). Effects of curcumin supplementation on sport and physical exercise: a systematic review. Critical reviews in food science and nutrition , 61 (6), 946–958. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2020.1749025
121. Pivari, F., Mingione, A., Brasacchio, C., & Soldati, L. (2019). Curcumin and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Prevention and Treatment. Nutrients , 11 (8), 1837. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081837
122. Ashtary-Larky, D., Rezaei Kelishadi, M., Bagheri, R., Moosavian, S. P., Wong, A., Davoodi, S. H., Khalili, P., Dutheil, F., Suzuki, K., & Asbaghi, O. (2021). The Effects of Nano-Curcumin Supplementation on Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Disease: A GRADE-Assessed Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Clinical Trials. Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland) , 10 (7), 1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10071015
123. Mata, I., Mata, S., Menezes, R., Faccioli, L. S., Bandeira, K. K., & Bosco, S. (2020). Benefits of turmeric supplementation for skin health in chronic diseases: a systematic review. Critical reviews in food science and nutrition , 1–15. Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2020.1798353