- Description
- Key Ingredients & Benefits
- Usage & Directions
- Quality Standards
- Warnings
- Sources
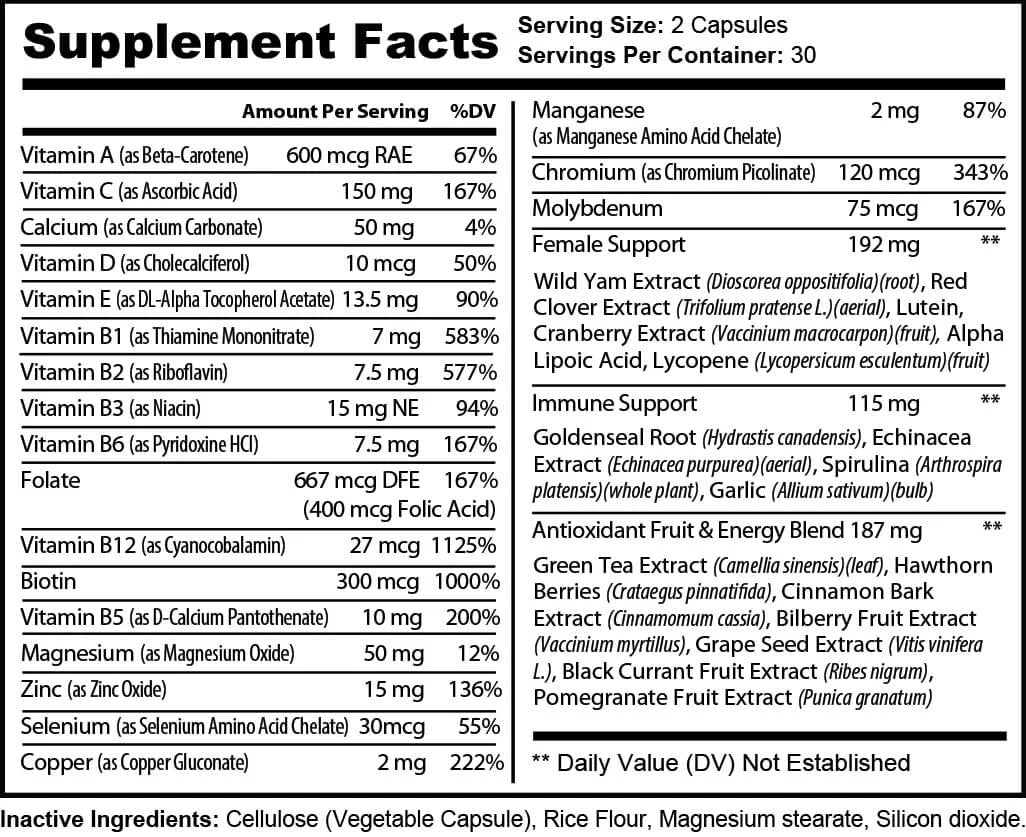
SHEvita Ultra for Women is a multi-benefit wellness formula designed to support energy, clarity, and vitality throughout your day. Packed with essential vitamins, minerals, adaptogens, and plant-based nutrients, it’s tailored to meet the unique demands of women’s active lifestyles.
-Daily Energy & Nutrient Support: B-vitamins, iron, and key minerals help fuel daily energy metabolism and support overall nourishment.
-Cycle-Friendly Ingredients: Includes nutrients traditionally used to support natural balance throughout the month.
-Beauty & Brain Blend: With biotin and choline to support skin, hair, and mental focus — from the inside out.
-Lifestyle-Driven Formula: Designed for women balancing movement, work, family, and wellness — all in one daily dose.
-Vitamin A : Supports vision, skin health, immune strength, and antioxidant function.
-Vitamin C : Boosts immunity, cardiovascular health, skin repair, and fat metabolism.
-Calcium & Vitamin D : Promote strong bones, muscle function, hormonal health, and exercise recovery.
-B-Vitamins (B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B12, Biotin) : Power your energy, nerve function, metabolism, and cognitive health.
-Magnesium & Zinc : Aid muscle relaxation, anxiety reduction, immune defense, and blood sugar regulation.
-Selenium & Copper : Provide antioxidant support, thyroid health, and cholesterol management.
Herbal & Natural Extracts
-Wild Yam & Red Clover Extracts : Promote hormonal balance, menopausal relief, and bone health.
Cranberry Extract : Supports urinary tract health and immune defense.
-Spirulina & Garlic : Reduce inflammation, improve gut health, and strengthen immunity.
-Green Tea & Grape Seed Extracts : Boost fat burning, cardiovascular health, and antioxidant activity.
-Cinnamon Bark & Pomegranate Extracts : Aid in blood sugar control, heart health, and digestion.
Targeted Nootropics & Antioxidants
-Alpha Lipoic Acid : Enhances blood sugar regulation, fat loss, and brain function.
-Echinacea & Goldenseal Root : Bolster immune response and digestive health.
-Lutein & Bilberry Extract : Protect vision and combat age-related eye issues.
Take 2 veggie capsules daily. For optimal results, combine with light exercise and a balanced diet. For maximum benefits, use consistently for at least 8 weeks.
- Third-party tested, GMP-certified, and made with premium, efficacious ingredients.
-*These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. -Tamper Seal: Use only if the seal is intact. Consult your health care practitioner if you are pregnant or nursing, taking medications, or have a medical condition, before taking this or any other product. -Store in a cool, dry place. Keep out of reach of children.
1.Sureda, A., & Pons, A. (2012). Arginine and citrulline supplementation in sports and exercise: ergogenic nutrients?. Medicine and sport science , 59 , 18–28. https://doi.org/10.1159/000341937
2.Szefel, J., Danielak, A., & Kruszewski, W. J. (2019). Metabolic pathways of L-arginine and therapeutic consequences in tumors. Advances in medical sciences , 64 (1), 104–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advms.2018.08.018
3.Rodrigues-Krause, J., Krause, M., Rocha, I., Umpierre, D., & Fayh, A. (2018). Association of l-Arginine Supplementation with Markers of Endothelial Function in Patients with Cardiovascular or Metabolic Disorders: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients , 11 (1), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11010015
4.Hu, S., Han, M., Rezaei, A., Li, D., Wu, G., & Ma, X. (2017). L-Arginine Modulates Glucose and Lipid Metabolism in Obesity and Diabetes. Current protein & peptide science , 18 (6), 599–608. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389203717666160627074017
9.Gasperi, V., Sibilano, M., Savini, I., & Catani, M. V. (2019). Niacin in the Central Nervous System: An Update of Biological Aspects and Clinical Applications. International journal of molecular sciences , 20 (4), 974. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20040974
10.Gentilcore D. (2016). Louis Sambon and the Clash of Pellagra Etiologies in Italy and the United States, 1905-14. Journal of the history of medicine and allied sciences , 71 (1), 19–42. https://doi.org/10.1093/jhmas/jrv002
11.Kirkland J. B. (2009). Niacin status and treatment-related leukemogenesis. Molecular cancer therapeutics , 8 (4), 725–732. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-09-0042
12.Hoskin, P., Rojas, A., & Saunders, M. (2009). Accelerated radiotherapy, carbogen, and nicotinamide (ARCON) in the treatment of advanced bladder cancer: mature results of a Phase II nonrandomized study. International journal of radiation oncology, biology, physics , 73 (5), 1425–1431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2008.06.1950
36. Khaing, W., Vallibhakara, S. A., Tantrakul, V., Vallibhakara, O., Rattanasiri, S., McEvoy, M., Attia, J., & Thakkinstian, A. (2017). Calcium and Vitamin D Supplementation for Prevention of Preeclampsia: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Nutrients , 9 (10), 1141. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9101141
37. Courteix, D., Jaffré, C., Lespessailles, E., & Benhamou, L. (2005). Cumulative effects of calcium supplementation and physical activity on bone accretion in premenarchal children: a double-blind randomised placebo-controlled trial. International journal of sports medicine , 26 (5), 332–338. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2004-821040
38. Ueland, P. M., McCann, A., Midttun, Ø., & Ulvik, A. (2017). Inflammation, vitamin B6 and related pathways. Molecular aspects of medicine , 53 , 10–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mam.2016.08.001
39. Bird R. P. (2018). The Emerging Role of Vitamin B6 in Inflammation and Carcinogenesis. Advances in food and nutrition research , 83 , 151–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.afnr.2017.11.004
40. Mascolo, E., & Vernì, F. (2020). Vitamin B6 and Diabetes: Relationship and Molecular Mechanisms. International journal of molecular sciences , 21 (10), 3669. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21103669
51. van de Lagemaat, E. E., de Groot, L., & van den Heuvel, E. (2019). Vitamin B12 in Relation to Oxidative Stress: A Systematic Review. Nutrients , 11 (2), 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11020482
52. Romain, M., Sviri, S., Linton, D. M., Stav, I., & van Heerden, P. V. (2016). The role of Vitamin B12 in the critically ill--a review. Anaesthesia and intensive care , 44 (4), 447–452. https://doi.org/10.1177/0310057X1604400410
53. Shipton, M. J., & Thachil, J. (2015). Vitamin B12 deficiency - A 21st century perspective . Clinical medicine (London, England) , 15 (2), 145–150. https://doi.org/10.7861/clinmedicine.15-2-145
60. Hoffer, L. J., Sher, K., Saboohi, F., Bernier, P., MacNamara, E. M., & Rinzler, D. (2003). N-acetyl-L-tyrosine as a tyrosine source in adult parenteral nutrition. JPEN. Journal of parenteral and enteral nutrition , 27 (6), 419–422. https://doi.org/10.1177/0148607103027006419
61. Ipson, B. R., & Fisher, A. L. (2016). Roles of the tyrosine isomers meta-tyrosine and ortho-tyrosine in oxidative stress. Ageing research reviews , 27 , 93–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2016.03.005
82. Langade, D., Kanchi, S., Salve, J., Debnath, K., & Ambegaokar, D. (2019). Efficacy and Safety of Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) Root Extract in Insomnia and Anxiety: A Double-blind, Randomized, Placebo-controlled Study. Cureus , 11 (9), e5797. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.5797
83. Bonilla, D. A., Moreno, Y., Gho, C., Petro, J. L., Odriozola-Martínez, A., & Kreider, R. B. (2021). Effects of Ashwagandha ( Withania somnifera ) on Physical Performance: Systematic Review and Bayesian Meta-Analysis. Journal of functional morphology and kinesiology , 6 (1), 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk6010020
90. Boyle, N. B., Lawton, C., & Dye, L. (2017). The Effects of Magnesium Supplementation on Subjective Anxiety and Stress-A Systematic Review. Nutrients , 9 (5), 429. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9050429
91. Verma, H., & Garg, R. (2017). Effect of magnesium supplementation on type 2 diabetes associated cardiovascular risk factors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of human nutrition and dietetics : the official journal of the British Dietetic Association , 30 (5), 621–633. https://doi.org/10.1111/jhn.12454
92. Thakur, K., Tomar, S. K., Singh, A. K., Mandal, S., & Arora, S. (2017). Riboflavin and health: A review of recent human research. Critical reviews in food science and nutrition , 57 (17), 3650–3660. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2016.1145104
93. Suwannasom, N., Kao, I., Pruß, A., Georgieva, R., & Bäumler, H. (2020). Riboflavin: The Health Benefits of a Forgotten Natural Vitamin. International journal of molecular sciences , 21 (3), 950. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030950
94. DiNicolantonio, J. J., Niazi, A. K., Lavie, C. J., O'Keefe, J. H., & Ventura, H. O. (2013). Thiamine supplementation for the treatment of heart failure: a review of the literature. Congestive heart failure (Greenwich, Conn.) , 19 (4), 214–222. https://doi.org/10.1111/chf.12037
95. Saedisomeolia, A., & Ashoori, M. (2018).Thiamine in Human Health: A Review of Current Evidences. Advances in food and nutrition research , 83 , 57–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.afnr.2017.11.002
96. Ragaller, V., Lebzien, P., Südekum, K. H., Hüther, L., & Flachowsky, G. (2011). Pantothenic acid in ruminant nutrition: a review. Journal of animal physiology and animal nutrition , 95 (1), 6–16. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0396.2010.01004.x
97. Carr, A. C., & Maggini, S. (2017). Vitamin C and Immune Function. Nutrients , 9 (11), 1211. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9111211
98. DePhillipo, N. N., Aman, Z. S., Kennedy, M. I., Begley, J. P., Moatshe, G., & LaPrade, R. F. (2018). Efficacy of Vitamin C Supplementation on Collagen Synthesis and Oxidative Stress After Musculoskeletal Injuries: A Systematic Review. Orthopaedic journal of sports medicine , 6 (10), 2325967118804544. https://doi.org/10.1177/2325967118804544
110. Hasani, H., Arab, A., Hadi, A., Pourmasoumi, M., Ghavami, A., & Miraghajani, M. (2019). Does ginger supplementation lower blood pressure? A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. Phytotherapy research : PTR , 33 (6), 1639–1647. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.6362
126. Kuchakulla, M., Narasimman, M., Soni, Y., Leong, J. Y., Patel, P., & Ramasamy, R. (2021). A systematic review and evidence-based analysis of ingredients in popular male testosterone and erectile dysfunction supplements. International journal of impotence research , 33 (3), 311–317. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41443-020-0285-x
127. Fang, J., & Zhang, Y. (2017). Icariin, an Anti-atherosclerotic Drug from Chinese Medicinal Herb Horny Goat Weed. Frontiers in pharmacology , 8 , 734. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2017.00734
13.Dording, C. M., Schettler, P. J., Dalton, E. D., Parkin, S. R., Walker, R. S., Fehling, K. B., Fava, M., & Mischoulon, D. (2015). A double-blind placebo-controlled trial of maca root as treatment for antidepressant-induced sexual dysfunction in women. Evidence-based complementary and alternative medicine : eCAM , 2015 , 949036. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/949036
128. Pathania, R., Chawla, P., Khan, H., Kaushik, R., & Khan, M. A. (2020). An assessment of potential nutritive and medicinal properties of Mucuna pruriens : a natural food legume. 3 Biotech , 10 (6), 261. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-02253-x
129. Rakesh B, Praveen N (2020) Chapter-10 biotechnological approaches for the production of l-DOPA: a novel and potent anti-Parkinson’s Drug from Mucuna pruriens (L.) DC. Chief Editor: 179
130. Majekodunmi, S. O., Oyagbemi, A. A., Umukoro, S., & Odeku, O. A. (2011). Evaluation of the anti-diabetic properties of Mucuna pruriens seed extract. Asian Pacific journal of tropical medicine , 4 (8), 632–636. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1995-7645(11)60161-2
135. Ferrini, M. G., Garcia, E., Abraham, A., Artaza, J. N., Nguyen, S., & Rajfer, J. (2018). Effect of ginger, Paullinia cupana, muira puama and l- citrulline, singly or in combination, on modulation of the inducible nitric oxide- NO-cGMP pathway in rat penile smooth muscle cells. Nitric oxide : biology and chemistry , 76 , 81–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.niox.2018.03.010
136. Sellami, M., Slimeni, O., Pokrywka, A., Kuvačić, G., D Hayes, L., Milic, M., & Padulo, J. (2018). Herbal medicine for sports: a review. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition , 15 , 14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12970-018-0218-y
137. Sellami, M., Slimeni, O., Pokrywka, A., Kuvačić, G., D Hayes, L., Milic, M., & Padulo, J. (2018). Herbal medicine for sports: a review. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition , 15 , 14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12970-018-0218-y
138. Saudan, C., Baume, N., Emery, C., Strahm, E., & Saugy, M. (2008). Short term impact of Tribulus terrestris intake on doping control analysis of endogenous steroids. Forensic science international , 178 (1), e7–e10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forsciint.2008.01.003
139. Palacios, S., Soler, E., Ramírez, M., Lilue, M., Khorsandi, D., & Losa, F. (2019). Effect of a multi-ingredient based food supplement on sexual function in women with low sexual desire. BMC women's health , 19 (1), 58. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12905-019-0755-9
140. Das, S., & Bisht, S. S. (2013). The bioactive and therapeutic potential of Hemidesmus indicus R. Br. (Indian Sarsaparilla) root. Phytotherapy research : PTR , 27 (6), 791–801. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.4788
141. She, T., Qu, L., Wang, L., Yang, X., Xu, S., Feng, J., Gao, Y., Zhao, C., Han, Y., Cai, S., & Shou, C. (2015). Sarsaparilla (Smilax Glabra Rhizome) Extract Inhibits Cancer Cell Growth by S Phase Arrest, Apoptosis, and Autophagy via Redox-Dependent ERK1/2 Pathway. Cancer prevention research (Philadelphia, Pa.) , 8 (5), 464–474. https://doi.org/10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-14-0372
142. Majumdar, S., Gupta, S., Prajapati, S. K., & Krishnamurthy, S. (2021). Neuro-nutraceutical potential of Asparagus racemosus: A review. Neurochemistry international , 145 , 105013. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2021.105013
143. Gombart, A. F., Pierre, A., & Maggini, S. (2020). A Review of Micronutrients and the Immune System-Working in Harmony to Reduce the Risk of Infection. Nutrients , 12 (1), 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12010236
144. Heffernan, S. M., Horner, K., De Vito, G., & Conway, G. E. (2019). The Role of Mineral and Trace Element Supplementation in Exercise and Athletic Performance: A Systematic Review. Nutrients , 11 (3), 696. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11030696
213. Mock DM. Biotin: From Nutrition to Therapeutics. J Nutr. 2017 Aug;147(8):1487-1492. doi: 10.3945/jn.116.238956. Epub 2017 Jul 12. PMID: 28701385; PMCID: PMC5525106.
214. Patel DP, Swink SM, Castelo-Soccio L. A Review of the Use of Biotin for Hair Loss. Skin Appendage Disord. 2017 Aug;3(3):166-169. doi: 10.1159/000462981. Epub 2017 Apr 27.